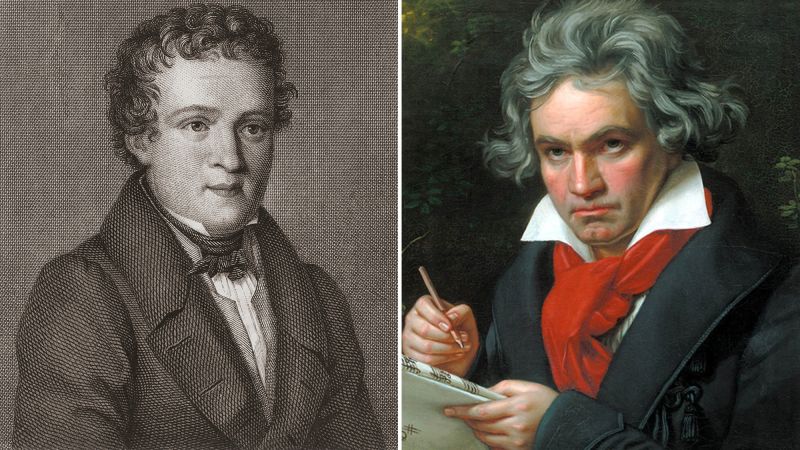In 2024, remarkable advances in scientific research have provided deeper insights into historical figures, unearthing stories and mysteries that had long been shrouded in ambiguity. The utilization of ancient DNA (aDNA) techniques has been particularly groundbreaking, offering new perspectives on well-known events and individuals. Among the notable revelations is the investigation into the archaeological site of Pompeii. For years, the tragic demise of victims during the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD had been interpreted in particular ways, but recent genetic analyses have radically transformed these narratives.
One striking case involves the discovery of genetic material from the remains of individuals believed to have been bonded, such as a mother cradling her son in their last moments. Contrary to previous assumptions, researchers revealed that this was actually an unrelated adult male offering comfort to a child during the disaster, thereby challenging our understanding of the human connections formed during such cataclysmic events. This unveils the rich, complex fabric of human relationships even in the direst circumstances.
Additionally, researchers have turned their attention to the enigmatic figure known as “Vittrup Man,” a Stone Age migrant whose body was unearthed from a peat bog in Vittrup, Denmark, almost 110 years ago. With innovative analytical techniques, scientists like Anders Fischer from the University of Gothenburg have pieced together a compelling narrative about this individual’s life. They determined that Vittrup Man was a hunter-gatherer who later embraced an agrarian lifestyle in Denmark, illustrating a significant cultural and dietary transition in his lifetime. Notably, the investigation establishes him as a first-generation immigrant, which adds a unique lens to our understanding of early human migration in Scandinavia.
Another intriguing exploration includes a skeleton found in a castle well in Norway. This investigation led to the connection of historical texts from the “Sverris Saga.” Researchers uncovered details such as the individual’s lineage and his burial practices, shedding light on the chaotic situations of war in the 12th century. Surprisingly, genetic studies indicated that the well’s victim was not a local but belonged to a different region, implying a deeper narrative of alliances and hostilities during that era.
The unveiling of historical figures does not solely revolve around ancient civilizations; it extends to more recent history as well. The case of Kaspar Hauser, an enigma of 19th-century Germany who was rumored to be a lost prince, continues to stir debates. Despite numerous studies, conflicting genetic tests left many questions unanswered. However, recent analysis of Hauser’s hair revealed that his DNA did not correspond with the royal family of Baden, once and for all putting to rest the speculation surrounding his royal lineage. Yet, this conclusion brings forth an even larger question: who was Kaspar Hauser?
Moving through the tapestry of time, we arrive at the celebrated composer Ludwig van Beethoven. His remarkable contributions to music, contrasted with a life fraught with affliction, prompted recent studies focusing on his health. In the latest findings, scientists have identified high levels of lead and other toxic substances in samples of Beethoven’s hair, suggesting that lead poisoning significantly impacted his health. This intersection of health and artistry adds layers to our comprehension of his masterpieces, intertwining the personal suffering he endured with the profound beauty of his music.
Shifting beyond individual figures, breakthroughs continued with investigations into familial legacies. A recent study into the family of George Washington illuminated the fate of long-forgotten relatives, demonstrating the potential of modern DNA techniques in unraveling historical mysteries. Additionally, findings unearthed concerning Thomas West, the first governor of Jamestown, highlighted the darker sides of colonial histories and familial secrets that shaped the life trajectories of many.
Finally, historical scientists like Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler have provided contemporary scholars with remarkable insights into our celestial past. By analyzing remnants of Brahe’s alchemical practices, researchers have unearthed evidence of sophisticated understandings of the natural world that challenge current perceptions of knowledge during the Renaissance.
As these various studies converge, they paint a broader picture of historical inquiry, emphasizing how technology evolves and influences our interpretations of the past, resulting in newfound admiration for those who came before us, and inspiring future generations of scholars and enthusiasts alike.